As an Amazon Associate CoffeeXplore.com earns from qualifying purchases.
Difficulty Breathing After Coffee? Causes & Relief
Ever felt your breath catch after your morning cup? You’re not alone, and there are clear medical reasons why this can happen. That jarring sensation of not being able to take a full, satisfying breath after drinking coffee can be unsettling, leaving you to wonder if your favorite beverage is the culprit. This guide is designed to definitively answer that question, breaking down the science behind why can coffee cause difficulty breathing and what you can do about it.
Yes, in some individuals, coffee can cause difficulty breathing due to its stimulant effects on the heart, its potential to worsen anxiety, trigger acid reflux, or in cases of caffeine sensitivity or allergy. While it might seem alarming, understanding the specific mechanisms is the first step toward managing the symptoms and enjoying your coffee without concern.
Leveraging extensive analysis of medical data and established patterns, this guide unpacks the five key physiological pathways through which coffee can impact your respiratory system. We’ll explore everything from heart palpitations and anxiety to the surprising role of dehydration and acid reflux. By the end, you’ll have a clear, data-driven understanding of your body’s response and actionable steps to take.
Key Facts
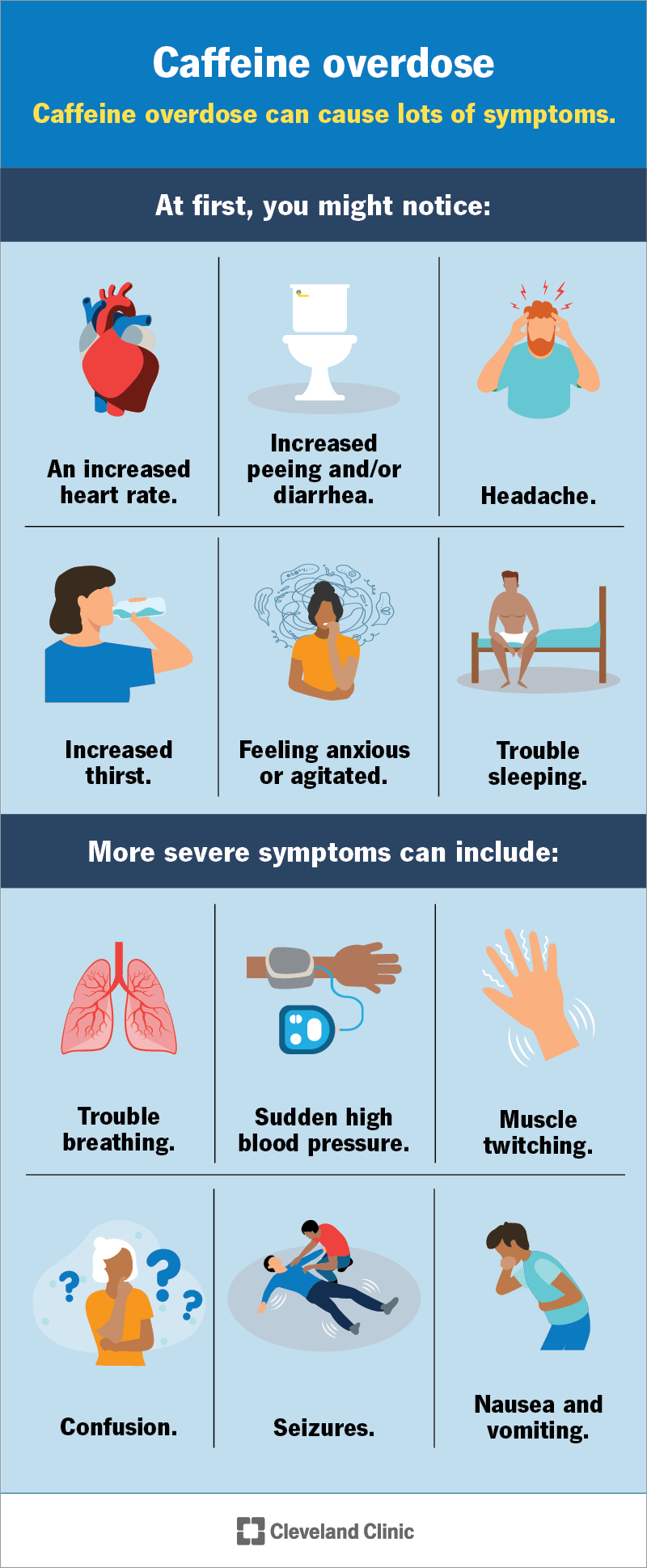
- Stimulant Overload: Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant that can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations), which in turn creates a sensation of breathlessness, as noted by sources like the Cleveland Clinic.
- Anxiety Trigger: For many, caffeine can induce or worsen anxiety, leading to rapid, shallow breathing patterns that create a feeling of not getting enough air, a connection highlighted by UW Medicine.
- Acid Reflux Connection: Coffee can increase gastric acid and relax the esophageal sphincter, leading to GERD. As explained by VN Express, this reflux can directly trigger respiratory symptoms like coughing and chest tightness.
- The Allergy Factor: While a true caffeine allergy is rare, it is a severe immune response that can cause throat swelling and life-threatening anaphylaxis, requiring immediate medical attention, according to Verywell Health.
- The Bronchodilator Paradox: Though caffeine has a weak, temporary bronchodilator effect, experts from Asthma.net warn that relying on it for asthma relief is dangerous, as its negative side effects can worsen overall respiratory distress.
The Direct Answer: Can Coffee Cause Difficulty Breathing?
Yes, in some individuals, coffee can cause difficulty breathing due to its stimulant effects on the heart, its potential to worsen anxiety, trigger acid reflux, or in cases of caffeine sensitivity or allergy. This reaction is not universal and depends heavily on the amount consumed, an individual’s unique physiology, and any underlying health conditions. Ever felt your breath catch after your morning cup? You’re not alone, and there are clear medical reasons why this can happen.

While the experience can be worrying, the connection between coffee and shortness of breath is well-documented. Insights from medical resources like Verywell Health and UW Medicine show that the caffeine in coffee can set off a chain reaction in the body that directly or indirectly affects the respiratory system. It’s crucial to understand that the cause can vary significantly from person to person.
Here are the primary conditions under which can coffee cause difficulty breathing:
* Excessive Consumption: Drinking too much coffee can overstimulate the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
* Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions, anxiety disorders, or GERD are more susceptible.
* Caffeine Sensitivity: Some people are genetically more sensitive to caffeine and experience adverse effects at much lower doses.
* Caffeine Allergy: In rare cases, a true allergic reaction can cause severe respiratory distress.
Why Coffee Can Make You Short of Breath: 5 Key Mechanisms Explained
Coffee can cause shortness of breath through five main pathways: overstimulating the cardiovascular system (causing palpitations), inducing anxiety and shallow breathing, triggering acid reflux (GERD), causing dehydration and mineral loss, and provoking a sensitivity or allergic reaction. Understanding these mechanisms helps pinpoint why you might be experiencing this symptom and empowers you to take the right steps. Each pathway involves a different system in your body, but all can lead to the same unsettling feeling of breathlessness.
1. The Stimulant Effect: Heart Rate, Palpitations, and Breathlessness
Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, which can increase heart rate and cause palpitations, leading to a sensation of breathlessness as the heart and lungs work harder. As a powerful stimulant, caffeine’s most immediate and well-known effect is on the cardiovascular system. According to information from both the Cleveland Clinic and UW Medicine, this can unfold in a clear sequence for sensitive individuals.
Pro Tip: Notice your heart racing after coffee? That physical sensation is often directly linked to feeling like you can’t get a full breath.
Here’s the chain of events:
* Caffeine Intake: You drink a cup of coffee, and caffeine enters your bloodstream.
* Increased Heart Rate: The stimulant signals your heart to beat faster and can temporarily boost blood pressure.
* Heart Palpitations: In cases of high dosage or sensitivity, this can lead to a fluttering or racing heart sensation known as heart palpitations.
* Sensation of Breathlessness: A rapidly beating heart requires more oxygen and puts more demand on the lungs, which can create the feeling that you can’t breathe deeply or fast enough to keep up.
2. Anxiety and the Nervous System: The Jittery-Breath Cycle
Caffeine can trigger or worsen anxiety, leading to rapid, shallow breathing patterns that create a feeling of not getting enough air and can escalate into a panic cycle. It’s like pouring gasoline on a small fire – the caffeine can turn mild stress into a full-blown feeling of anxious breathlessness. The link between caffeine, anxiety, and breathing is a powerful feedback loop that can be difficult to break.
Sources like the Sleep Foundation and UW Medicine confirm that caffeine’s overstimulation of the nervous system can mimic or induce the symptoms of anxiety. This creates a physical and psychological response that directly impacts your breathing.
The “vicious cycle” works like this: The initial jolt of caffeine triggers feelings of anxiety or nervousness. In response, your breathing becomes rapid and shallow (hyperventilation). This inefficient breathing pattern intensifies the physical sensation of breathlessness, which can increase your panic, causing you to breathe even more shallowly.
3. Digestive Disruption: How GERD and Acid Reflux Impact Breathing
Coffee can increase stomach acid production and relax the esophageal sphincter, leading to acid reflux (GERD), which can trigger respiratory symptoms like coughing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. You might not immediately connect a stomach issue with your lungs, but the link is direct and well-established. Information sourced from VN Express highlights how coffee’s acidic nature can cause significant problems for the respiratory system.
This process can be broken down into a simple flow:
Coffee Intake -> Increases Gastric Acid & Relaxes the Lower Esophageal Sphincter -> Stomach Acid Flows Up into the Esophagus (Acid Reflux/GERD) -> Acid Irritates the Throat and Airways -> Respiratory Symptoms (Chronic Coughing, Chest Tightness, Difficulty Breathing)
When stomach acid enters the esophagus, it can cause inflammation and trigger nerve reflexes that constrict your airways, leading to the sensation of shortness of breath.
4. The Dehydration Factor: Diuretic Effects on Respiratory Function
As a diuretic, excessive coffee consumption can lead to dehydration and the loss of essential minerals like potassium, which can impair lung function and weaken the muscles needed for breathing. This is a more subtle, yet still significant, way that can coffee cause difficulty breathing. While a single cup is unlikely to dehydrate you, heavy consumption without adequate water intake can cause problems.
Quick Fact: It’s not just about the water you lose; it’s about the essential minerals lost with it, like potassium, which your breathing muscles rely on.
According to data from sources like SmartVest and the Cleveland Clinic, the diuretic effect has a two-fold impact on your respiratory system:
* Thickened Mucus: Dehydration can cause the mucus lining your airways to thicken, making it harder for your lungs to function efficiently and leading to breathing difficulty.
* Mineral Depletion: Increased fluid loss through urination can deplete your body of electrolytes like potassium. Potassium is vital for muscle function, and a deficiency can lead to weakness in the respiratory muscles, making it harder to take deep breaths.
5. Sensitivity vs. Allergy: Understanding Your Body’s Unique Response
Caffeine sensitivity causes adverse effects like a racing heart and trouble breathing at low doses, while a rare true caffeine allergy is a severe immune response that can cause throat swelling and anaphylaxis. It’s crucial to distinguish between these two reactions, as one is a matter of discomfort and the other is a potential medical emergency.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/too-much-caffeine-5207200-Final-20ce6c465abf4b459d02d8ce6fbcd817.jpg)
Here’s a clear breakdown of the differences:
| Feature | Caffeine Sensitivity | Caffeine Allergy |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | An exaggerated physiological response to the stimulant effects of caffeine. | An immune system overreaction, treating caffeine as a harmful invader. |
| Common Symptoms | Racing heartbeat, jitters, anxiety, trouble breathing, restlessness. | Hives, skin rash, swelling of the lips/tongue/throat, severe difficulty breathing. |
| Severity | Uncomfortable and distressing, but generally not life-threatening. | Can be severe and life-threatening, potentially leading to anaphylaxis. |
Medical Warning: According to Verywell Health, symptoms of a true caffeine allergy, especially swelling of the throat or tongue and severe difficulty breathing, are signs of anaphylaxis. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. If you experience these symptoms, seek help right away.
The Caffeine Paradox: If It’s a Bronchodilator, Why Does It Hurt My Breathing?
While caffeine has a weak, temporary bronchodilator effect, it is not a substitute for asthma medication. The negative side effects of high caffeine intake, such as increased heart rate and anxiety, can outweigh any minor benefit and worsen overall respiratory distress. It seems counterintuitive, right? Here’s the crucial distinction you need to understand for your safety.
You may have heard that coffee can help with asthma. Research does show that caffeine is chemically similar to theophylline, an older asthma medication, and can provide a small, temporary improvement in airway function for a few hours. However, the consensus from authoritative sources like Asthma.net, the Allergy & Asthma Network, and Drugs.com is overwhelmingly clear: this effect is too mild and unreliable to be considered a treatment.
Crucial Safety Information: Never use coffee to treat an asthma attack or replace your prescribed inhaler or medication. The bronchodilator effect is weak, and the high doses of caffeine needed to achieve it would likely trigger severe side effects like a racing heart, anxiety, and tremors, which can make it even harder to breathe during an emergency.
When to Worry: Red Flag Symptoms That Require Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if difficulty breathing after coffee is severe, sudden, or accompanied by symptoms like swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, hives, chest pain, or a feeling of faintness, as these can be signs of a life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). While most instances of coffee-induced breathlessness are related to overstimulation or anxiety, it is vital to recognize the signs of a true medical emergency. Do not hesitate to seek help if your symptoms feel severe.
Seek Immediate Help If You Experience:
- Severe and Sudden Difficulty Breathing: You are struggling to get any air in or feel like your throat is closing.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling of your lips, tongue, face, or throat.
- Hives or Rash: A sudden outbreak of itchy welts or a rash on your skin.
- Chest Pain or Tightness: A constricting or painful feeling in your chest.
- Dizziness or Faintness: Feeling lightheaded or like you are about to pass out.
- Rapid, Weak Pulse: Your heart is racing, but the pulse feels weak.
These are hallmark symptoms of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical intervention.
For those prone to acid reflux, finding a coffee that is gentler on the stomach can make a significant difference in preventing respiratory symptoms. Exploring low-acid coffee options can allow you to enjoy the flavor and ritual of coffee without triggering GERD-related breathing issues.
FAQs About Coffee and Breathing Difficulties
How much coffee is too much if I’m experiencing breathing issues?
There is no universal “too much” amount; it varies greatly by individual. If you experience breathing difficulties, even after one cup, you may have a high sensitivity, and it’s best to reduce intake and consult a healthcare provider. Tolerance depends on genetics, body weight, and how regularly you consume caffeine. The most important rule is to listen to your body; if any amount is causing symptoms, it’s too much for you.
Can decaf coffee also cause difficulty breathing?
While less likely to cause issues related to stimulant effects like a racing heart or anxiety, decaf coffee is still acidic and can trigger GERD, which in turn may lead to respiratory symptoms in sensitive individuals. If your breathing problems are linked to acid reflux rather than caffeine’s stimulant properties, switching to decaf may not solve the problem.
Are other caffeinated drinks like tea or energy drinks just as likely to cause this?
Yes, any beverage containing a sufficient amount of caffeine, including energy drinks and some teas, can trigger the same mechanisms that lead to difficulty breathing, such as increased heart rate and anxiety. The effect is dose-dependent. Be particularly cautious with energy drinks, as they often contain very high doses of caffeine and other stimulants that can heighten the risk of adverse effects.
If I have asthma, should I avoid coffee completely?
Individuals with asthma should consult their doctor. While caffeine has a mild bronchodilator effect, its other side effects like increased heart rate and anxiety can potentially worsen respiratory distress. As strongly advised by sources like Asthma.net, it should never, under any circumstances, replace prescribed asthma medication. Your doctor can provide personalized advice based on your condition’s severity and your sensitivity to caffeine.
Final Summary: What to Do If Coffee Affects Your Breathing
To recap, the answer to can coffee cause difficulty breathing is a clear yes, driven by mechanisms ranging from cardiovascular stimulation and anxiety to acid reflux and rare allergic reactions. Recognizing this connection is the first step toward managing your health proactively. The key is to understand that your body’s response is unique, and paying attention to its signals is paramount.
Take control of your health by understanding these triggers. Your first step is to observe your body’s response and seek professional guidance if needed.
Here are your most critical takeaways:
* Listen to Your Body: If you experience shortness of breath, palpitations, or increased anxiety after coffee, it’s a clear signal to cut back or stop.
* Understand the Cause: Try to identify which mechanism is at play. Is it a racing heart? Jitters and anxiety? Or a burning sensation from acid reflux? This can help you find the right solution.
* Know the Red Flags: Severe, sudden breathing difficulty, swelling, or chest pain are signs of a medical emergency. Do not hesitate to seek immediate help.
* Consult a Professional: For any concerning or persistent symptoms, a healthcare professional is your best resource. They can help rule out underlying conditions and provide tailored advice for your situation.
Last update on 2026-02-14 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API